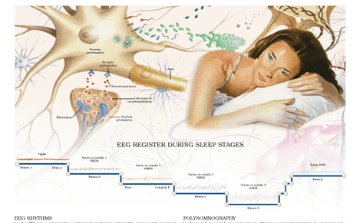
Overview
The time (hours) spent during sleep or the time a person takes before falling asleep does not define insomnia. Individuals have varying needs in terms of sleep satisfaction. Insomnia manifests in different general forms as described below.
- Problems in falling asleep- This is a sleep-onset condition where the affected persons have problems in falling asleep. This happens because of failure to let the mind relax, continuous thinking, and continuous worries. Sometimes, your body is unable to sleep at the usual sleep time. This occurs because of the lack of synchronization between your biological clock and the earth’s time of darkness and light. This problem, which is a known circadian rhythm disorder, mainly occurs in young adults and adolescents.
- Problems in staying asleep- This sleep maintenance problem is likely to affect older people compared to younger people. Persons with this problem fall asleep without any problems, but get up some hours later. They have problems in sleeping again when they wake up. They may also experience unsatisfactory and restless sleep because of waking up frequently during sleep.
- Early morning awakening- It is a common problem in all people and may indicate depression.
The Many Forms of Insomnia
 Essentially, insomnia refers to the indications of troubled sleep instead of an illness. The key factors here include symptom duration and the causative factors.
Essentially, insomnia refers to the indications of troubled sleep instead of an illness. The key factors here include symptom duration and the causative factors.
Transient Insomnia
It is the commonest form of insomnia affecting about 58 percent of adults. Persons suffering from this condition have symptoms that last for at most 7 days. A number of factors can trigger this form of insomnia. Some of these factors include jet lag, medication, worries, and stress. There are different short-term remedies for the uncomfortable symptoms associated with this condition. These remedies include natural medications and relaxation techniques. The aim is to prevent the symptoms from becoming self-perpetuating. A good example would be taking caffeine or starting a sleeping pattern to prevent sleep.
Short-Term Insomnia
People with this condition have symptoms that occur for 7 to 21 days. This duration is long enough to make disturbed sleep a concern considering the associated risks. Sleep problems induced by anxiety and stress fall under this category. The best treatment is to address the underlying causes, but other techniques are also available. For instance, you can assess your evening eating practices, lifestyle factors (exercise and health), and sleeping environment.
Chronic Insomnia
 It is the most devastating form of insomnia characterized by symptoms that last for over three weeks. In this case, affected persons should look for professional advice from medical practitioners. Sufferers can also use home-based techniques such as keeping a sleep diary to identify adverse factors or patterns in the evening or in bedtime activities. While drugs offer a temporary relief from chronic insomnia, they can build tolerance and cause addiction.
It is the most devastating form of insomnia characterized by symptoms that last for over three weeks. In this case, affected persons should look for professional advice from medical practitioners. Sufferers can also use home-based techniques such as keeping a sleep diary to identify adverse factors or patterns in the evening or in bedtime activities. While drugs offer a temporary relief from chronic insomnia, they can build tolerance and cause addiction.
Mental Illness
Individuals with this form of insomnia have long-lasting symptoms associated with depression, brain chemistry changes, and other mental problems. Some of the conditions accompanied by this form of insomnia include bipolar disorder and schizophrenia. Professional supervision is essential during treatment, especially if the treatment involves medication.
Fatal Familial
This is an extremely rare genetically inherited insomnia. It results from mutant proteins and is fatal between seven and thirty-six months after the first symptoms. The chance of inheriting this condition from a carrier parent is 50/50, but patients do not show symptoms until they reach middle age, mostly around 50. The condition worsens leading to total inability to fall asleep and finally death. Luckily, only 28 families have been confirmed to have the responsible gene worldwide.
Do you want to find an effective Insomnia treatment? Check out our top rated Insomnia products